Sperm Donation Bank in Chennai
There are certain situations when a man is unable to produce sperms of the right quantity or quality OR the woman is not able to produce eggs of acceptable quality OR both. In such cases, pregnancy is still possible through donor sperm or donor egg or donor embryos.
When does one use a sperm donor?
A sperm donor can be used in the types of situations listed below;
- If tests done on the semen and testicular tissue show that a patient’s testes do not produce sperm.
- Presence of a genetic disease that might pass on to the offspring
- In situations where the male has a sexually transmitted disease for LGBTQ couples.
How is donor sperm organized?
At PSFC, we set up Sperm Donation Bank in Chennai with recognized and registered international standards to evaluate sperm and frozen for storage later.
Sperm samples are tested for infectious diseases like Hepatitis B, C and HIV. We work with renowned sperm banks to deliver the sperm of your choice and profile with strict confidentiality.

EGG (OOCYTE) DONATION
HISTORY:
The first baby was born due to oocyte donation three years after the first IVF baby was born. Oocyte donation was initially made for women who experience premature menopause; gradually, the procedure became a solution for older women.
When is Egg Donation Needed?
There are four main reasons people choose oocyte (egg) donation as a means of having a baby,
- Several failed attempts happened in IVF, and recurrent miscarriages caused by poor egg quality or embryo development.
- Premature menopause or other factors causing cessation of egg production, such as hereditary diseases, endometriosis, and surgery done on the ovaries resulting in significant loss of ovarian tissue.
- Infertile couples, where the woman is not permitted to use drugs necessary to induce oocyte production.
- Older women who have entered menopause – Arguments against oocyte donation usually focus on these patients. A 65-year-old Romanian woman records as the most aged woman who had a baby through this method.
In egg (Oocyte) donation, the baby carries half of the family’s genetic makeup. In addition, the parents experience the psychosocial changes resulting from sharing the pregnancy and delivery. The source of the donor egg is usually at an age where the chances of chromosomal anomalies are meagre.
However, the donor’s age does not protect the mother from complications during her pregnancy. The age of the woman carrying the baby and her overall health affect how the pregnancy will progress. Even if ovaries stop egg production, the uterus can have a baby to term.
The uterus can be reprogrammed with oral or injectable drugs to prepare the organ for implantation and pregnancy. Chances of pregnancy are similar to a younger woman using her eggs. Sometimes pregnancy rates can even be higher for these women.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE OOCYTE?
We operate with a registered Sperm Donation Bank in Chennai; donors will be selected according to the criteria listed below and will be strictly confidential.
- Before a woman gets accepted into the donor oocyte program, she will be examined by the Bank’s gynaecologist.
- A psychological evaluation will be done thoroughly on the prospective donor if necessary.
- In addition, the recipient will be privy to the donor’s age, physical health and education status.
- Any information revealing the donor’s identity will be confidential under a code name only hospital administrators can access.
- Likewise, the recipient’s identity is also kept confidential. In this regard, we follow ART 2022 guidelines issued by Govt of India Ministry of Health.
Profile of Donor:
- Must be between the ages of 20 and 32.
- She should not have any marked physical characteristics, such as an unusual noise that might distinguish her.
- Donors can select according to the recipient’s race, colour and blood type; the donor’s intelligence level should be average or above average.
- There must be no physical restrictions against procedures such as controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and egg collection.
- A person who has known genetic diseases in the family or has lost a baby for unexplained reasons cannot be accepted into the program as a donor.
Egg collection does not reduce the oocytes available to the woman; the procedure does not affect the donor’s fertility and age of menopause onset. Therefore, her chances of achieving pregnancy will be no more after she donates her eggs.
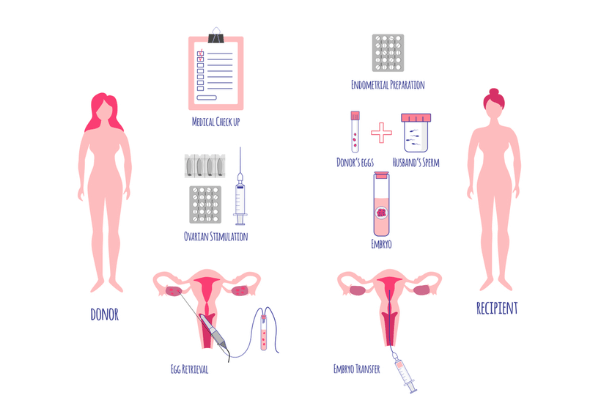
Briefly, the donor goes through two main steps.
The first prepares the ovaries to stimulate increased egg production, and the second collects the eggs that develop.
The woman will start the drug regimen on the second or third day of menstruation; after approximately 8-12 days of stimulation, eggs will be collected and marks the end of the donor’s role in the process. After that, her eggs will be inseminated by the sperm obtained from the recipient’s husband, and the resulting embryos will be transferred to the recipient’s uterus.
Preparation of the recipient
Two methods exist to prepare her uterus if the recipient menstruates regularly. Either the recipient’s cycle is synchronised to that of the donor using a combination of hormonal supplements, or they temporarily suppress the recipient’s ovulation. Doctors usually use GnRH analogue drug type for this purpose.
After the woman gets her period, she takes estrogen hormone orally; later, Progesterone is added on the day the eggs are collected. This way, the endometrium acquires the necessary thickness for the embryo to implant.
Preliminary tests are done before the procedure summarised below.
- A mock transfer will be used to transfer the embryos with the same type of catheter. Menopausal women, in particular, may have a narrow or deformed cervix. The cervix can be dilated under anaesthesia if necessary.
- Gynaecological ultrasonography
- A pelvic exam where the doctor may take a pap smear or order a colposcopy for a more detailed examination.
- Hysteroscopy (if the clinician cannot get a clear view of the uterine lining through ultrasonography)
- Preparation of the endometrium (the uterine lining that is shed every month) using drugs. The recipient’s endometrial thickness should reach at least 8mm for a successful pregnancy.